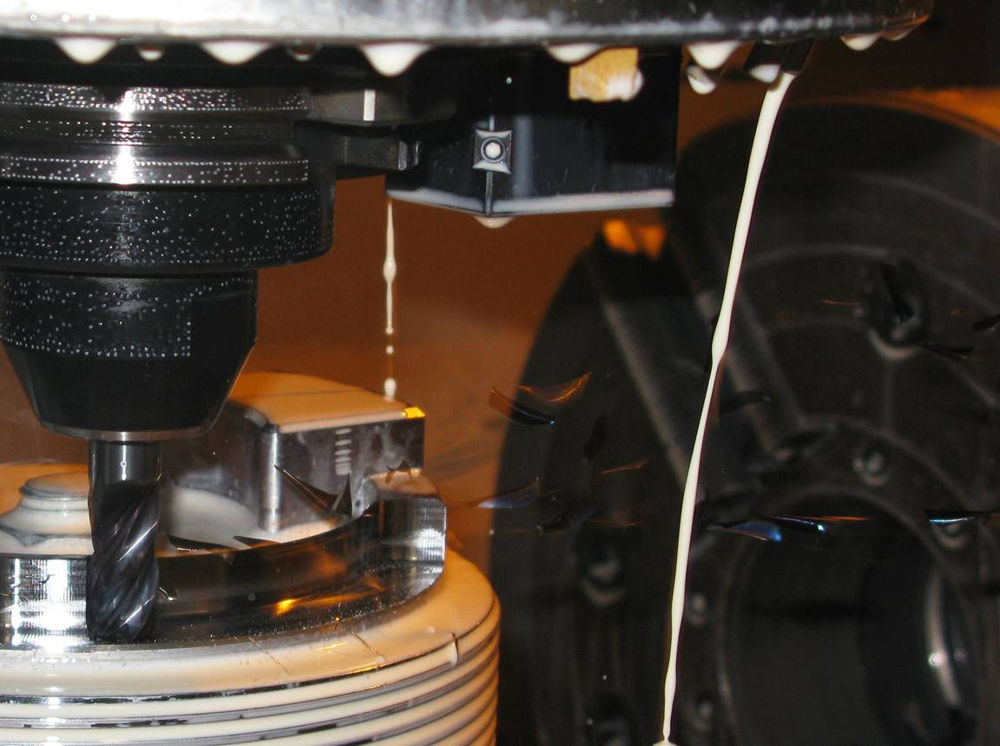
Introduction
Working with CNC machines that are not precise and versatile can make the machining process challenging. For this reason, engineers opt for non-cut-and-dried vertical milling machines. However, that does not necessarily mean that selecting any CNC machine cutting tools is restricted to how well they perform in terms of accuracy and precision.
One needs to be mindful of several factors when selecting such tools. Failure to do so may result in a poor-quality end product that no manufacturing unit wishes to produce.
Here are five important considerations when selecting CNC cutting tools. Take a look.
1. CNC Machining Tool Configurations
A CNC machine features different configuration types. Many CNC machining tools offer multiple features. In other words, many CNC tools can be configured for multiple tasks to be handled by a single cutting machine. This feature further reduces the time needed to complete the entire machining process.
Multi-feature CNC machines can also save considerable time, which may go into changing the tools for different requirements. However, it should be noted that different configurations are designed for different workpiece types and materials. Thus, engineers must know which tool configuration they need for their workpieces.
2. Materials And Features Of The Workpiece
The tool to be used is highly dependent on the material of the workpiece one is operating on. Experts recommend different CNC machining cutting tools for different material types. For example, the Stecker machine works with aluminum, grey iron castings, and ductile iron.
Even within these materials, aluminum tends to have the highest machinability and SFM (surface feet per minute). Therefore, engineers and manufacturers should understand the materials and features of their workpieces.
3. The Capacity of CNC Machines
Tooling machines should be shortlisted depending on the production volume of one's projects. CNC machines can use the majority of cutting tools. However, that does not equate to the enhanced efficiency of those CNC machines. Experts recommend that a higher horsepower machine allows engineers to use multiple combo tools suitable for performing various functions.
In addition, the casting of the machine is also an important consideration. Case in point: smaller castings do not require the help of hosts to move them around, unlike large castings. Running multiple tool parts on a pallet can save considerable time that may go into changing the tool parts.
In other words, selecting the right cutting tool is all about matching the machine's ability and availability to the requirements of projects.
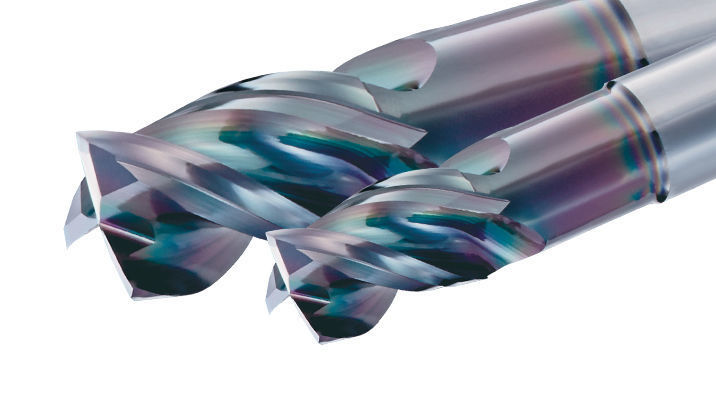
4. Materials Used in the Cutting Tools
Engineers have to work with different materials as per project needs. One must note that the materials used for designing cutting tools can enhance the longevity and finishing of the end product. Case in point: some cutting tools can be developed using materials that are more durable than others. Most cutting tools are made of solid carbide because solid carbide creates a durable cutting tool.
However, polycrystalline diamond-tipped (PCD-tipped) tools can create the hardest and the most reliable cutting tools. It is worth noting that the tool life for a drilling tool made from PCD is around four times longer than that of ones made from solid carbide. The PCD-tipped tools are also known to be 25 times faster than the carbide-cutting tools. In addition, the precision of the PCD-tipped tools is also better.
However, one of the important points to be wary of when selecting materials for cutting tools is the cost. While PCD-tipped tools may seem like the best option for cutting high-precision edges, they come with an expensive price tag. Thus, solid carbide is a less expensive option that costs 75 times less than PCD-tipped tools.
5. Feed and Spindle Speed
The feed and spindle speed are two technical terms that one needs to understand to create better end products. Feed speed is technically the rate at which the work material moves inside the cutter. Feed speed is always dependent on the spindle speed. Failure to use an accurate feed and spindle speed can even burn the workpiece.
Engineers must mathematically determine the optimal feed speed before operating on the workpiece to avoid unwanted results. It is important to note that feed speed is not the same as cutting speed, which is the peripheral speed of the tool. In other words, feed speed is associated with the movement of the cutting tool, while cutting speed is associated with the tools.
Conclusion
Engineers tend to work with designs with higher geometric complexity and different materials. As a result, it goes without saying that when working with computerized cutting tools, accuracy is the utmost priority. However, the tool's accuracy is not the only aspect that makes or breaks the efficiency of CNC machining processes.
One needs to be mindful of various aspects before deciding on the right tools for precise cutting. Awareness of the aforementioned factors is essential to enhance the efficiency and end product.
About the Author:
Vincent Hua
Vincent Hua is the Marketing Manager at TSINFA. He is passionate about helping people understand high-end and complex manufacturing processes. Besides writing and contributing his insights, Vincent is very keen on technological innovation that helps build highly precise and stable CNC Machinery.












 Contact Us
Contact Us  Product Search
Product Search 